In Mostã¢â‚¬â€¹ Circumstances, All Fixed Costs Can Be Eliminated by Outsourcing a Product.
Toll of Quality (COQ)
Quality Glossary Definition: Toll of quality
Toll of quality (COQ) is defined as a methodology that allows an organisation to determine the extent to which its resources are used for activities that prevent poor quality, that appraise the quality of the organisation's products or services, and that result from internal and external failures. Having such information allows an organization to determine the potential savings to exist gained by implementing process improvements.
- Toll of poor quality (COPQ)
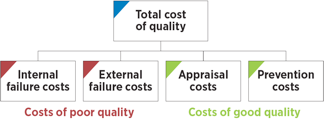
- Appraisal costs
- Internal failure costs
- External failure costs
- Prevention costs
- COQ and organizational objectives
- COQ resources
What is Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)?
Cost of poor quality (COPQ) is defined as the costs associated with providing poor quality products or services. There are three categories:
- Appraisal costs are costs incurred to determine the caste of conformance to quality requirements.
- Internal failure costs are costs associated with defects found before the customer receives the product or service.
- External failure costs are costs associated with defects found after the customer receives the production or service.
Quality-related activities that incur costs may exist divided into prevention costs, appraisement costs, and internal and external failure costs.
Appraisal costs
Appraisal costs are associated with measuring and monitoring activities related to quality. These costs are associated with the suppliers' and customers' evaluation of purchased materials, processes, products, and services to ensure that they conform to specifications. They could include:
- Verification: Checking of incoming fabric, process setup, and products against agreed specifications
- Quality audits: Confirmation that the quality system is performance correctly
- Supplier rating: Assessment and approval of suppliers of products and services
Cost of Quality on ASQ® Television set
Cost of Quality: What is it?

As well, click hither to watch a special video on the cost of poor quality published by the ASQ Audit Segmentation.
Internal failure costs
Internal failure costs are incurred to remedy defects discovered before the product or service is delivered to the client. These costs occur when the results of work neglect to reach blueprint quality standards and are detected before they are transferred to the client. They could include:
- Waste: Performance of unnecessary work or belongings of stock equally a result of errors, poor arrangement, or communication
- Scrap: Defective product or material that cannot be repaired, used, or sold
- Rework or rectification: Correction of defective textile or errors
- Failure analysis: Activity required to establish the causes of internal product or service failure
External failure costs
External failure costs are incurred to remedy defects discovered past customers. These costs occur when products or services that fail to attain design quality standards are not detected until after transfer to the customer. They could include:
- Repairs and servicing: Of both returned products and those in the field
- Warranty claims: Failed products that are replaced or services that are re-performed nether a guarantee
- Complaints: All work and costs associated with handling and servicing customers' complaints
- Returns: Handling and investigation of rejected or recalled products, including transport costs
Prevention costs
Prevention costs are incurred to prevent or avoid quality problems. These costs are associated with the pattern, implementation, and maintenance of the quality management system. They are planned and incurred before actual operation, and they could include:
- Product or service requirements: Establishment of specifications for incoming materials, processes, finished products, and services
- Quality planning: Creation of plans for quality, reliability, operations, product, and inspection
- Quality assurance: Creation and maintenance of the quality system
- Training: Development, preparation, and maintenance of programs
Toll of quality and organizational objectives
The costs of doing a quality task, conducting quality improvements, and achieving goals must be carefully managed then that the long-term effect of quality on the organization is a desirable ane.
These costs must exist a true mensurate of the quality effort, and they are best determined from an assay of the costs of quality. Such an analysis provides a method of assessing the effectiveness of the management of quality and a means of determining problem areas, opportunities, savings, and action priorities.
Toll of quality is also an important communication tool. Philip Crosby demonstrated what a powerful tool it could be to raise sensation of the importance of quality. He referred to the measure as the "price of nonconformance" and argued that organizations choose to pay for poor quality.
Many organizations will have true quality-related costs every bit high equally 15-20% of sales revenue, some going as high equally 40% of total operations. A general rule of thumb is that costs of poor quality in a thriving company will be about ten-15% of operations. Effective quality improvement programs tin can reduce this substantially, thus making a straight contribution to profits.
The quality cost organisation, in one case established, should get dynamic and have a positive impact on the achievement of the system's mission, goals, and objectives.
Cost of Quality Example
Cost of Quality resources
You can too search manufactures, case studies, and publications for toll of quality resources.
Using Toll of Quality to Meliorate Business Results (PDF) Since centering improvement efforts on cost of quality, CRC Industries has reduced failure dollars as a per centum of sales and saved hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Cost of Quality: Why More Organizations Do Non Use It Finer (World Conference on Quality and Comeback) Quality managers in organizations that do not rails toll of quality cite every bit reasons a lack of management support for quality control, time and cost of COQ tracking, lack of knowledge of how to rail data, and lack of basic toll information.
The Tip of the Iceberg (Quality Progress) A Six Sigma initiative focused on reducing the costs of poor quality enables management to reap increased customer satisfaction and bottom-line results.
Price of Quality (COQ): Which Collection System Should Be Used? (World Conference on Quality and Comeback) This article identifies the various COQ systems bachelor and the benefits and disadvantages of using each organization.
Adapted fromThe ASQ Quality Improvement Pocket Guide: Basic History, Concepts, Tools, and Relationships, ASQ Quality Press.
mcknightasherettle36.blogspot.com
Source: https://asq.org/quality-resources/cost-of-quality
0 Response to "In Mostã¢â‚¬â€¹ Circumstances, All Fixed Costs Can Be Eliminated by Outsourcing a Product."
Post a Comment